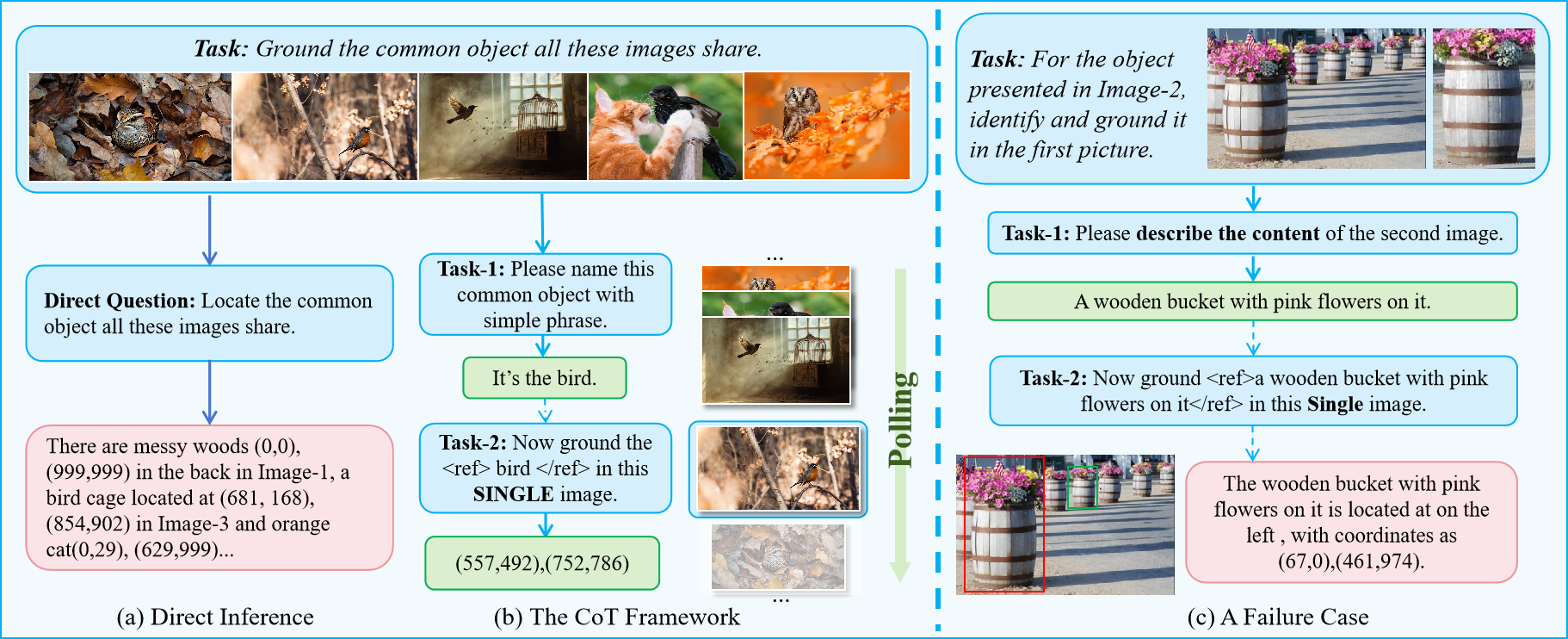
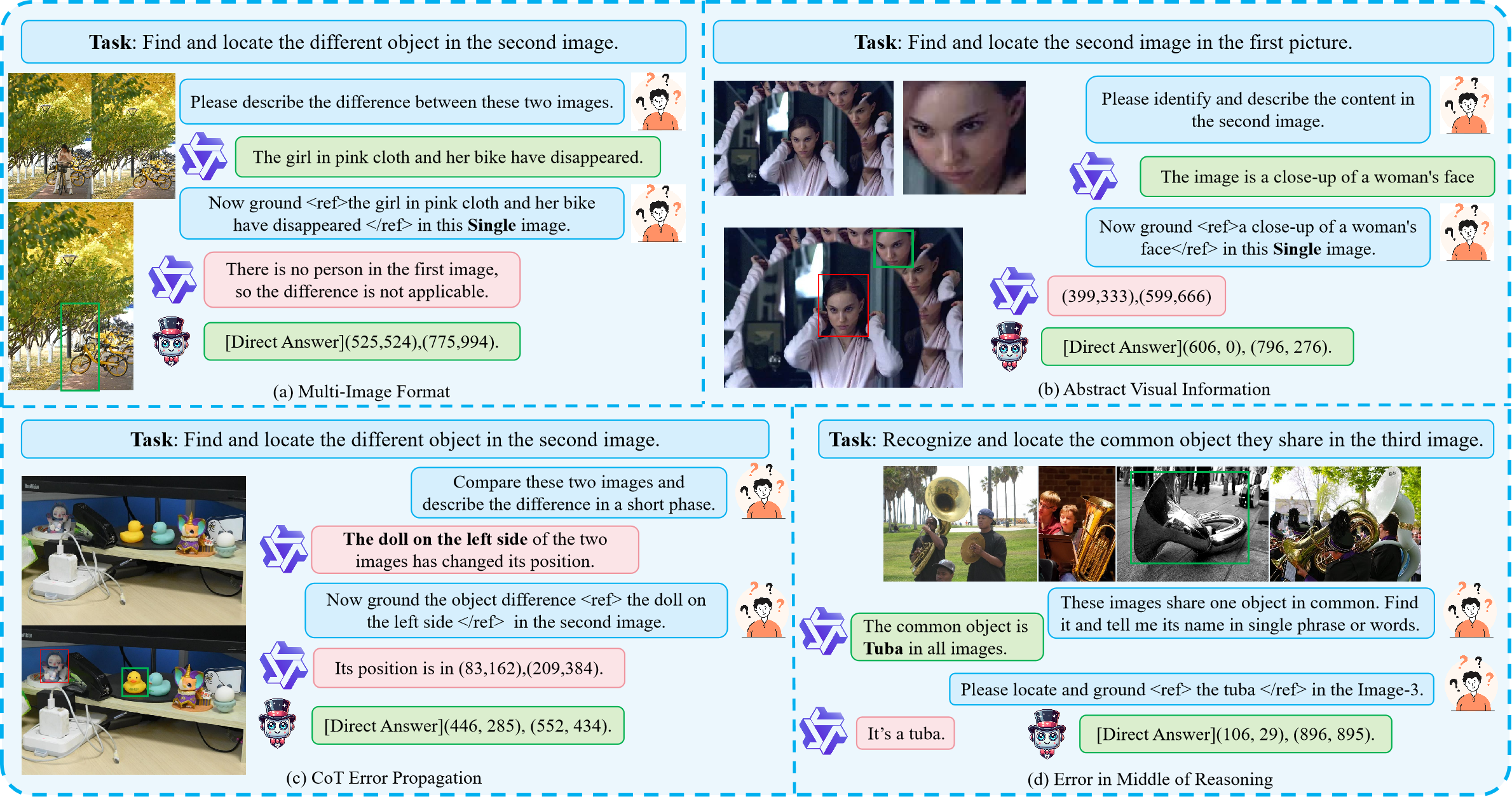
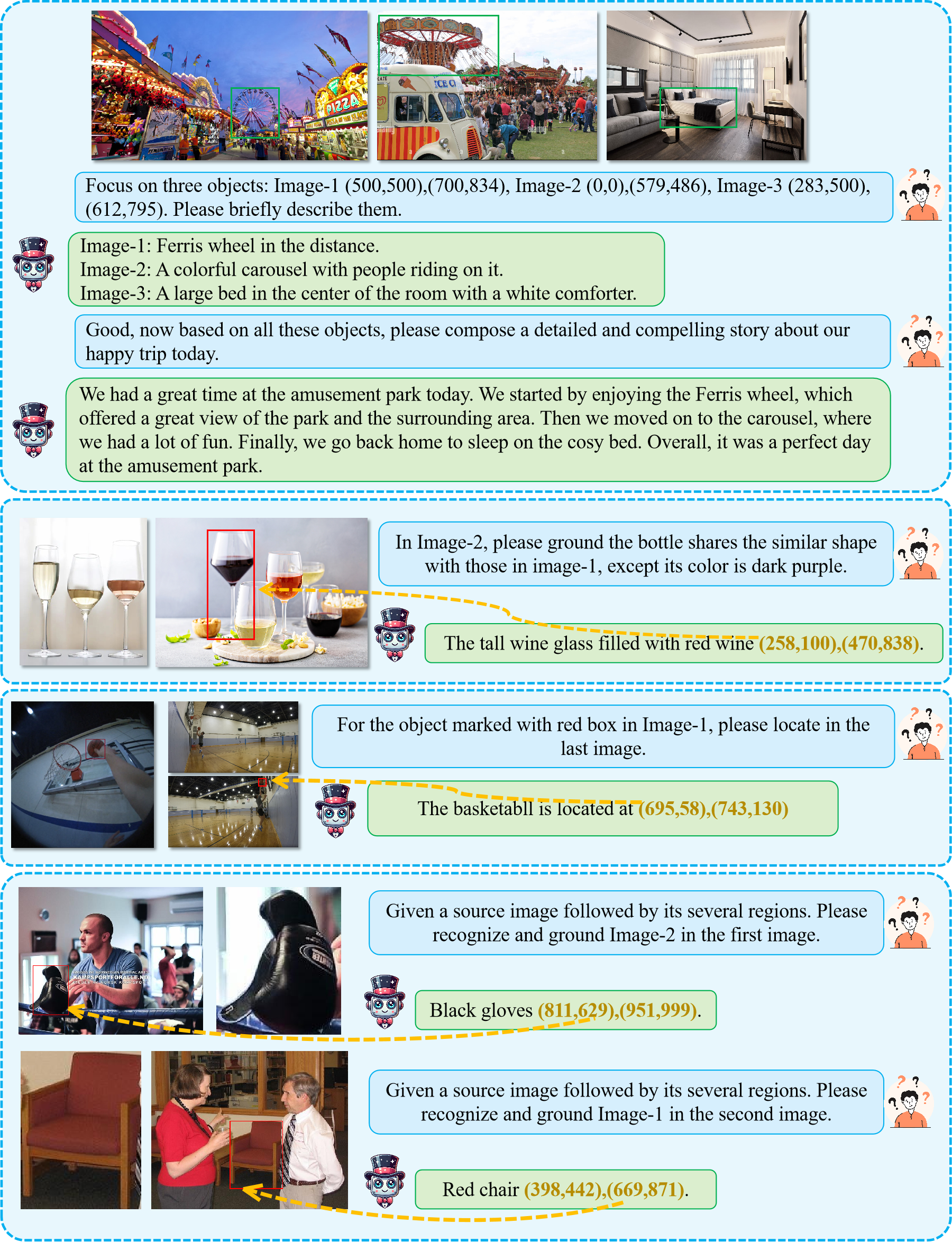
As shown above, based on whether the task involves explicit reference requirements, multi-image grounding tasks can be further categorized into two types: Spontaneous Grounding and Referential Grounding. Spontaneous Grounding refers to recognizing and grounding the target object in corresponding images without explicitly pointing it out. Unlike the conventional Reference Expression Comprehension task that explicitly refer to the target object, Spontaneous Grounding typically utilizes the relationships between multiple images as contextual cues to autonomously identify and localize the objects to be grounded~(e.g., finding and locating differences between images). Referential Grounding, on the other hand, requires an explicit reference to the target object. As mentioned earlier, such references can take the form of arbitrary combinations of images and textual descriptions.
Noticeably, our proposed multi-image grounding paradigm could potentially be a general paradigm unifying diverse tasks traditionally dominated by specialized expert models, for instance object tracking, vehicle/person re-identification, partial graph matching and etc, facilitating more general and versatile machine intelligence. Moreover, its innate multi-image characteristics circumvents the need for additional visual modules specializedly processing visual input queries (VisionLLM v2, Griffon v2), rendering a more general architecture.